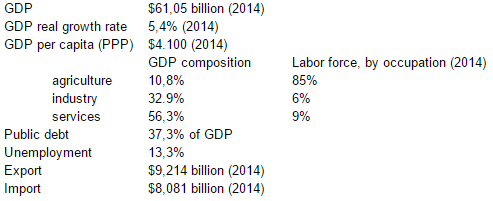
The Zambian economy is a fast growing economy, especially in the last ten years. The real GDP grows with an annual average of 6,7%. The most important source of national income is the mining industry, especially copper mining in the Copperbelt area. Since the privatization of the copper mines in the 1990’s, the mining industry significantly increased the copper mining output resulting in economic growth. Due to the higher copper prices the copper output increased steadily resulting in Zambia being the number one copper mining country for several years. However, in the last years the Democratic Republic of Congo has overtaken Zambia as largest copper producer. Zambia is very dependent on copper output, this makes the Zambian economy vulnerable to changes in this sector. Despite the promising growth numbers, poverty is still a major issue. Approximately 64% of the Zambian people live under the poverty line, 42% are considered to be extremely poor. The Copperbelt and Lusaka are relatively prosperous with a fairly low poverty incidence of 22% and 34% respectively. In the more rural areas agriculture is the most common source of income, in these areas poverty rates above 70% are no exception. The gap between the rich and the poor has grown despite economic growth. As a result, the poorer layer in society has little or no budget to spend on building materials and housing. Therefore doing research on low-cost building materials can be very useful, especially for this population group.
According to projections from the United Nations, Zambia's population will increase 941% by the end of the century, the highest growth rate of any country in the world. Zambia is one of the most urbanised countries in sub-Saharan Africa, with 35% of the population living in urban areas, particularly in Lusaka. The frantic growth rate is placing a heavy burden on housing, roads, water, sanitation, healthcare and energy provision. (Smith, 2011)